
CNG & CBG – The Future of Clean Energy
Explore complete production technology, standards, government policies, global initiatives and business models for Compressed Bio Gas.
CBG Production Technology
Complete biogas-to-CBG conversion system using anaerobic digestion, purification and high-pressure compression.
CBG (Compressed Bio Gas) is produced through the anaerobic digestion of agricultural residue, cattle dung, sugarcane press mud, MSW, sewage waste and industrial organic residue. The resulting biogas is purified to remove CO₂, H₂S and moisture, achieving **methane content above 90%**, then compressed up to **250 bar** for bottling.
Anaerobic Digestion Stages
Four-step biological process that converts organic material into methane-rich biogas.
1. Hydrolysis
2. Acidogenesis
3. Acetogenesis
4. Methanogenesis
Hydrogen Sulfide Removal
H₂S is corrosive and reduces calorific value — hence removal is essential.
Process Flow Diagram
Anaerobic Digestion Technologies
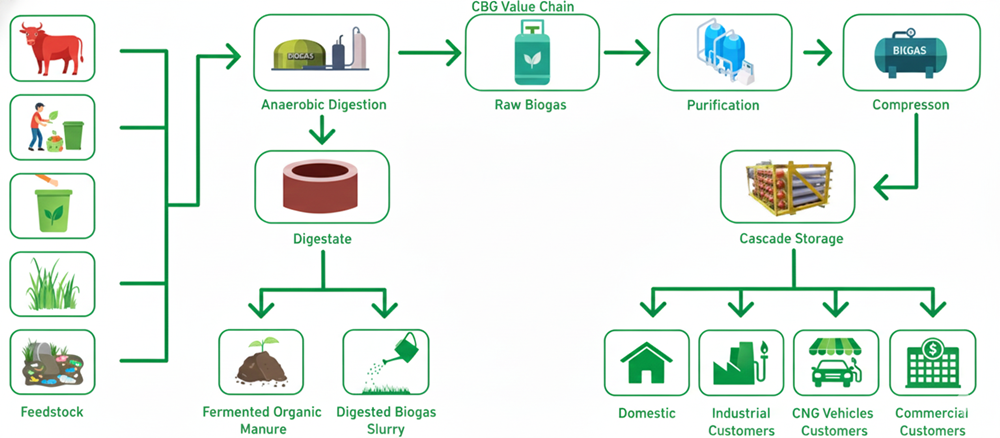
Different types of digesters used to convert organic biomass into biogas efficiently.
Continuously Stirred Tank Reactor (CSTR)
A CSTR digester is continuously fed with organic material and provides uniform mixing, ensuring **steady and predictable biogas output**. Ideal for **large-scale commercial CBG plants** where consistent production is crucial.
Advantages
- Efficient digestion
- Handles different dry matter levels
- Can digest energy crops
- Good solids degradation due to mixing
Disadvantages
- Complex digestion process
- High capital cost
- Requires skilled operators
Horizontal Plug-Flow Reactor
Organic feedstock flows horizontally through a long rectangular chamber with progressive gas injection. Suitable for **medium-scale plants with semi-solid feed**.
Advantages
- Inexpensive construction
- Easily adapted to hydraulic flushing
- Simple management
Disadvantages
- Hard top makes solid removal difficult
- Membrane covers are sensitive to weather
Batch-Type Digesters
The digester is filled once, sealed, and left for the full retention period. Most common in **low-cost rural systems**.
Advantages
- Cheapest & simplest to build
- Ideal where raw material supply is uncertain
Disadvantages
- Biogas production is uneven
- Requires multiple digesters to maintain continuous gas flow
- Occupies more land area
Covered Lagoon Digesters
Essentially a lined pond with a flexible cover that captures biogas. Best suited for **large livestock farms, dairy waste, and agricultural sludge**.
Advantages
- Very low cost
- Large volume capacity
- Simple construction
- Ideal for farms & large waste streams
Disadvantages
- Poor mixing
- Lower energy yield
- Cover maintenance can affect lifespan
Detailed Digester Comparison
A CSTR digester is continuously fed with organic material and provides uniform mixing, ensuring **steady and predictable biogas output**. Ideal for **large-scale commercial CBG plants** where consistent production is crucial.
Advantages
- Efficient digestion
- Handles different dry matter levels
- Can digest energy crops
- Good solids degradation due to mixing
Disadvantages
- Complex digestion process
- High capital cost
- Requires skilled operators
Organic feedstock flows horizontally through a long rectangular chamber with progressive gas injection. Suitable for **medium-scale plants with semi-solid feed**.
Advantages
- Inexpensive construction
- Easily adapted to hydraulic flushing
- Simple management
Disadvantages
- Hard top makes solid removal difficult
- Membrane covers are sensitive to weather
The digester is filled once, sealed, and left for the full retention period. Most common in **low-cost rural systems**.
Advantages
- Cheapest & simplest to build
- Ideal where raw material supply is uncertain
Disadvantages
- Biogas production is uneven
- Requires multiple digesters to maintain continuous gas flow
- Occupies more land area
Essentially a lined pond with a flexible cover that captures biogas. Best suited for **large livestock farms, dairy waste, and agricultural sludge**.
Advantages
- Very low cost
- Large volume capacity
- Simple construction
- Ideal for farms & large waste streams
Disadvantages
- Poor mixing
- Lower energy yield
- Cover maintenance can affect lifespan
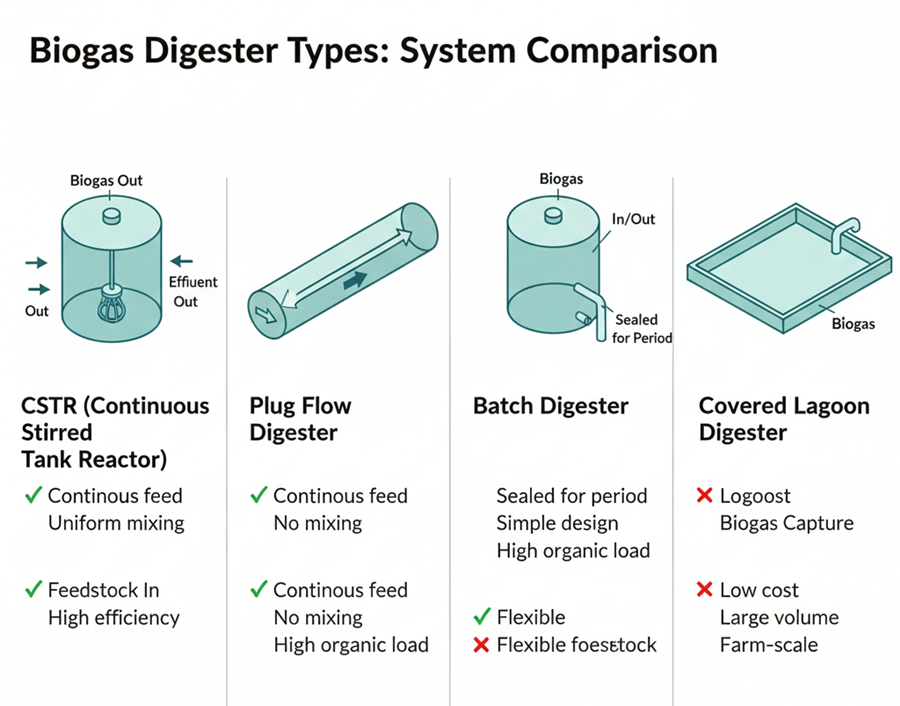
Biogas Purification Technologies
Technologies used to upgrade raw biogas into high-purity CBG with >90% methane content.
Pressure Swing Adsorption (PSA)
PSA is one of the most widely used technologies in India for large-scale biogas upgrading. It separates **carbon dioxide (CO₂) from methane** by adsorbing CO₂ at high pressure on materials like activated carbon or zeolites. When pressure is reduced, the adsorbent regenerates and becomes ready for the next cycle.
Advantages
- High methane recovery
- Low operating cost after installation
- Reliable and suitable for large plants
Disadvantages
- Requires pre-removal of H₂S and moisture
- High capital cost
- Requires stable biogas flow
Vacuum Swing Adsorption (VSA)
VSA is a non-cryogenic gas separation technology that uses **molecular sieves** to selectively adsorb CO₂ at near-ambient pressure. A vacuum is applied to regenerate the adsorbent. Effective for medium-scale CBG plants.
Advantages
- Lower power consumption than PSA
- Efficient CO₂ separation
- Good for medium-sized installations
Disadvantages
- Vacuum pumps require maintenance
- Less methane purity compared to PSA
Water Scrubbing
CO₂ is more soluble in water than methane. Biogas is passed through a **high-pressure water column**, dissolving CO₂ and H₂S, and producing methane-rich gas. Works best when water can be recirculated.
Advantages
- Simple and robust technology
- Removes both CO₂ and H₂S
- Low chemical usage
Disadvantages
- High water consumption
- Requires cooling for efficiency
Membrane Separation
Gas passes through **semi-permeable membranes**. CO₂, water vapor and ammonia permeate faster than methane, enriching methane concentration. Typically used in 2 or 3-stage membrane systems. Ideal for modular installations.
Advantages
- Compact, modular and scalable
- Low maintenance
- High purity levels achievable
Disadvantages
- Sensitive to impurities
- Requires pre-filtration
Chemical Scrubbing (MEA System)
Monoethylamine (MEA) solution **chemically reacts with CO₂**, forming a stable compound. The solution is regenerated by heating, releasing CO₂ and allowing MEA reuse. It delivers extremely high methane purities.
Advantages
- Very high CO₂ removal efficiency
- High methane purity (> 98%)
Disadvantages
- Energy-intensive regeneration
- Chemical handling required
Cryogenic Upgrading
CO₂ is liquefied at very low temperatures while methane remains gaseous. This allows high purity methane separation. Used in large industrial-scale bio-LNG or CBG production.
Advantages
- Extremely high methane purity
- CO₂ byproduct can be reused
Disadvantages
- Very high energy requirement
- High CAPEX equipment
Detailed Technology Explanation
PSA is one of the most widely used technologies in India for large-scale biogas upgrading. It separates **carbon dioxide (CO₂) from methane** by adsorbing CO₂ at high pressure on materials like activated carbon or zeolites. When pressure is reduced, the adsorbent regenerates and becomes ready for the next cycle.
Advantages
- High methane recovery
- Low operating cost after installation
- Reliable and suitable for large plants
Disadvantages
- Requires pre-removal of H₂S and moisture
- High capital cost
- Requires stable biogas flow
VSA is a non-cryogenic gas separation technology that uses **molecular sieves** to selectively adsorb CO₂ at near-ambient pressure. A vacuum is applied to regenerate the adsorbent. Effective for medium-scale CBG plants.
Advantages
- Lower power consumption than PSA
- Efficient CO₂ separation
- Good for medium-sized installations
Disadvantages
- Vacuum pumps require maintenance
- Less methane purity compared to PSA
CO₂ is more soluble in water than methane. Biogas is passed through a **high-pressure water column**, dissolving CO₂ and H₂S, and producing methane-rich gas. Works best when water can be recirculated.
Advantages
- Simple and robust technology
- Removes both CO₂ and H₂S
- Low chemical usage
Disadvantages
- High water consumption
- Requires cooling for efficiency
Gas passes through **semi-permeable membranes**. CO₂, water vapor and ammonia permeate faster than methane, enriching methane concentration. Typically used in 2 or 3-stage membrane systems. Ideal for modular installations.
Advantages
- Compact, modular and scalable
- Low maintenance
- High purity levels achievable
Disadvantages
- Sensitive to impurities
- Requires pre-filtration
Monoethylamine (MEA) solution **chemically reacts with CO₂**, forming a stable compound. The solution is regenerated by heating, releasing CO₂ and allowing MEA reuse. It delivers extremely high methane purities.
Advantages
- Very high CO₂ removal efficiency
- High methane purity (> 98%)
Disadvantages
- Energy-intensive regeneration
- Chemical handling required
CO₂ is liquefied at very low temperatures while methane remains gaseous. This allows high purity methane separation. Used in large industrial-scale bio-LNG or CBG production.
Advantages
- Extremely high methane purity
- CO₂ byproduct can be reused
Disadvantages
- Very high energy requirement
- High CAPEX equipment
Moisture & H₂S Management
- Biological fixation
- Iron chloride dosing
- Water scrubbing
- Activated carbon filters
- Iron oxide/hydroxide media
- Sodium hydroxide scrubbing
Purification System Flow Diagram
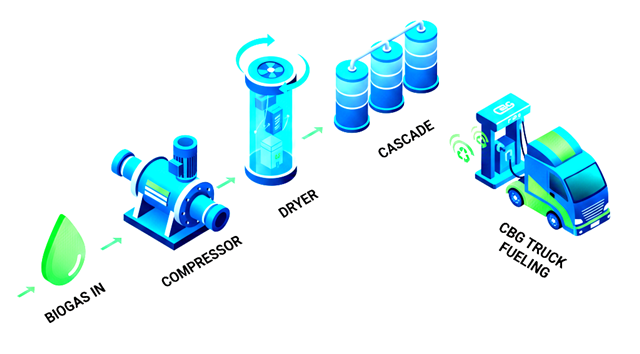
CBG Bottling & High-Pressure Storage
Purified biogas is compressed and stored safely in steel or composite cascades according to national standards.
High Pressure Compression (250 Bar)
Cascade Storage (3000 L / Higher Capacity)
Steel Cylinder Cascades (IS 7285)
Composite Cylinder Cascades (IS 15935)
Cylinder Types & Standards
| Type | Material | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Type 1 | All-steel cylinder | Highest weight, most economical |
| Type 2 | Steel with hoop-wrapped fiberglass | Moderate weight reduction |
| Type 3 | Aluminum liner with full composite wrap | Much lighter, improved durability |
| Type 4 | Plastic liner + full composite wrap | Lightest & most efficient |
- IS 7285 — Specifications for steel gas cylinders.
- IS 15935 — Specifications for composite pressure vessels.
- Transport guidelines must follow Petroleum & Explosives Safety Organization (PESO) norms.
- CBG delivered to fuel retail outlets must meetIS 16087:2016 quality standards.
- Only approved cascades with valid test certificates permitted
- Safety valves and burst discs mandatory
- Pressure testing required periodically
Compression & Cascade Diagram
CBG Quality Standards — IS 16087:2016
Specifications defined by the Bureau of Indian Standards for Compressed Bio Gas used as automotive fuel.
| Characteristic | Requirement |
|---|---|
| Methane (CH₄), Minimum | 90.0% |
| Carbon Dioxide (CO₂), Maximum | 4% |
| CO₂ + Nitrogen (N₂) + Oxygen (O₂), Maximum | 10% |
| Oxygen (O₂), Maximum | 0.5% |
| Total Sulphur (Including H₂S), Maximum | 20 mg/m³ |
| Moisture, Maximum | 5 mg/m³ |
Additional BIS Requirements
- CBG must be free from liquids across all operating temperatures & pressures.
- CBG must be free from dust, dirt, and any particulate matter.
- Gas must be odorized similar to local distribution gas (as per IS 15319).
- Compressed and stored at ~250 Bar for transportation to OMC retail outlets.
CBG Specification Chart
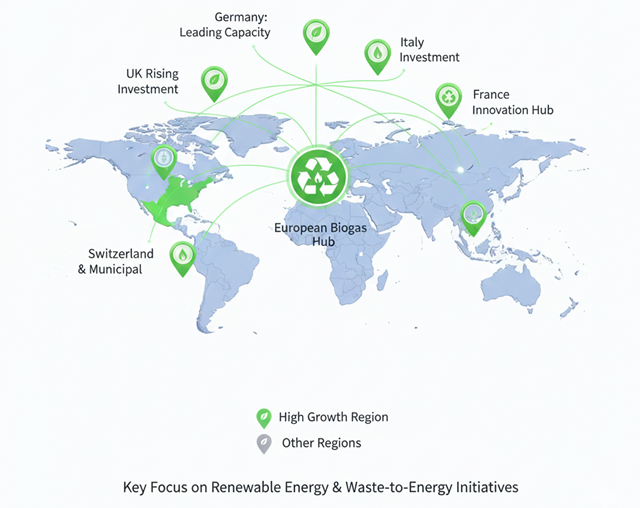
Global Initiatives in Biogas & CBG
Countries worldwide are rapidly adopting biogas for transportation, grid injection and renewable energy generation.
Germany
Italy
United Kingdom
France
Switzerland
European Biogas Strategy
Across Europe, biogas is used for **grid injection**, **electricity generation**, **district heating**, and **transportation fuel**. Countries provide strong policy frameworks, education programs, and technology support to accelerate renewable gas adoption.
Global Biogas Growth Map
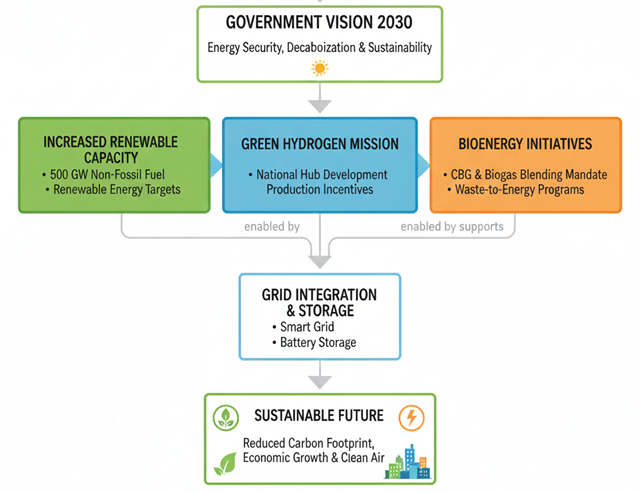
Government Policy Support
Strong national policies drive the adoption of Compressed Bio Gas across India.
National Biofuel Policy (2018)
GOBAR-DHAN Scheme
MNRE Central Financial Assistance (CFA)
India's Energy and Sustainability Vision
India is one of the fastest-growing economies with rapidly increasing energy demand. The government has outlined major reforms to strengthen energy access, security and sustainability:
- Increase natural gas contribution in India's energy mix from 6.5% → 15%
- Reduce crude oil imports by 10%
- Double farmers’ income through biomass supply and residue monetisation
- Promote circular economy & decentralized rural energy
India’s Renewable Energy Roadmap
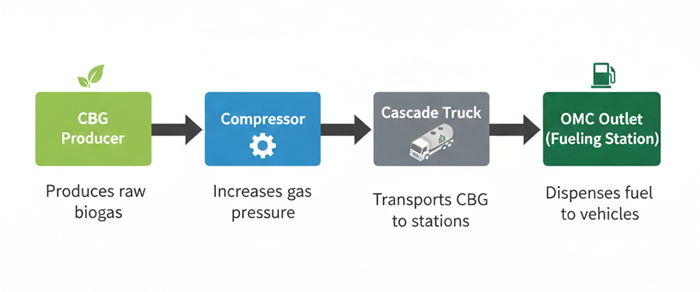
Business Model for CBG Production Under SATAT
The SATAT initiative establishes a structured and profitable ecosystem connecting farmers, CBG plant owners, and Oil Marketing Companies.
The SATAT (Sustainable Alternative Towards Affordable Transportation) scheme outlines a business model where **CBG producers supply compressed bio-gas to Oil Marketing Companies (OMCs)** for use as a renewable automotive fuel. The model creates value across the chain — from farmers supplying biomass to OMCs retailing green fuel.
Benefits of the SATAT Business Model
Reduces natural gas & crude oil imports
Promotes rural economy & employment generation
Utilizes agricultural waste & MSW responsibly
Supports Swachh Bharat Mission
Reduces pollution & carbon emissions
Generates bio-manure as a valuable by-product
CBG Production & Distribution Flow
1. Biomass / Waste Collection
Agricultural residue, cattle dung, press mud, MSW, and sewage waste are collected locally.
2. Transportation to Plant
Biomass delivered to CBG plants located close to farming or waste generation hubs.
3. Biogas Production
Anaerobic digestion technology converts biomass into raw biogas (~55–60% methane).
4. Purification & Upgrading
Biogas is purified (H₂S, CO₂, moisture removal) to increase methane concentration above 90%.
5. Compression to 250 Bar
Purified biogas is compressed into CBG using high-pressure compressors.
6. Cascade Filling
Compressed gas stored in steel or composite cascades (3000 L and above).
7. Delivery to OMC Retail Outlets
Cascades transported to fuel stations within a radius of 25 km as per SATAT guidelines.
8. CBG Dispensing
CBG dispensed as a green automotive fuel similar to CNG, meeting IS 16087:2016 standards.
Revenue Streams for CBG Plant Owners
CBG Sale to OMCs
OMCs (HPCL, BPCL, IOCL) purchase CBG under long-term assured offtake agreements.
Sale of Fermented Organic Manure (FOM)
Bio-manure generated during digestion sold to farmers, improving soil fertility.
Tipping Fees (MSW-based Plants)
Municipal bodies may pay processing fees for waste disposal services.
Carbon Credits
CBG plants may earn carbon credit income due to methane capture & emission reduction.
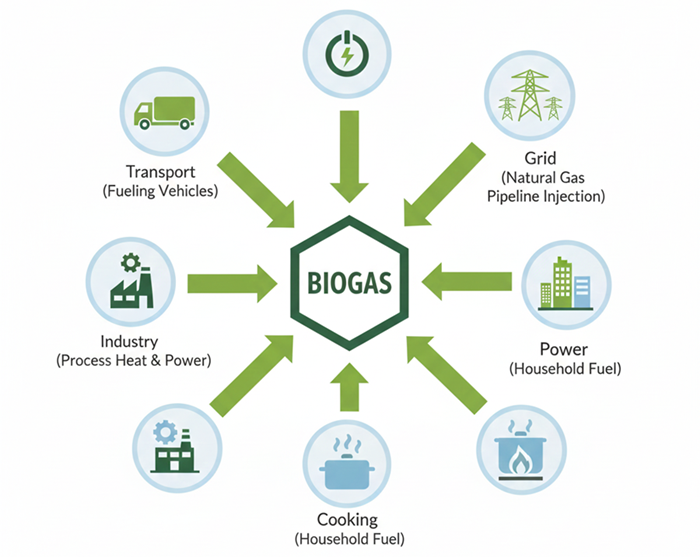
Applications of CNG / CBG
Clean, renewable and versatile — CBG unlocks value for transport, industry and power sectors.
Transportation
Used in cars, auto rickshaws, buses, and commercial vehicles as a clean and economical alternative to petrol and diesel.
Industrial Applications
Industries use CBG as a reliable and efficient fuel for heating, boilers, furnaces, and thermal applications.
Power Generation
CBG is used to produce electricity through gas engines and turbines, reducing emissions dramatically.
Commercial Cooking
Hotels, restaurants, and institutions use CBG for clean and efficient cooking solutions.
Agricultural Applications
Bio-manure from CBG plants improves soil health, replacing chemical fertilizers.
Grid Injection (Future Roadmap)
Upgraded biomethane can be injected into natural gas pipelines, widely practiced in Europe.
Usage Scenarios Diagram
CNG vs Petrol
A cleaner and more economical choice for modern transportation.
| Feature | CNG | Petrol |
|---|---|---|
| Emissions | Significantly lower emissions | Releases harmful pollutants |
| Cost | 40–50% cheaper fuel cost | High running cost |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, minimal pollution | High carbon & particulate emissions |
| Maintenance | Cleaner combustion → lower maintenance | Higher engine deposits |
| Safety | Lighter than air — dissipates quickly | Highly flammable, pools on ground |
| Fuel Availability | Rapidly expanding in India | Widely available, but costly |
Why CNG Is the Better Choice
- ✓ Cuts emissions by up to 90%
- ✓ Reduces operating costs drastically
- ✓ Improves engine life due to clean combustion
- ✓ Safer handling & lower fire risk
Switch to Smarter, Cleaner Energy
Explore CBG solutions, production technology, or partnership opportunities — our team will guide you with expert support.
Contact UsDiscover how CBG can transform your business.
